Brain Anatomy
Robin Smithuis
Radiology department, Alrijne Hospital Leiden, the Netherlands.
Publicationdate
Axial anatomy
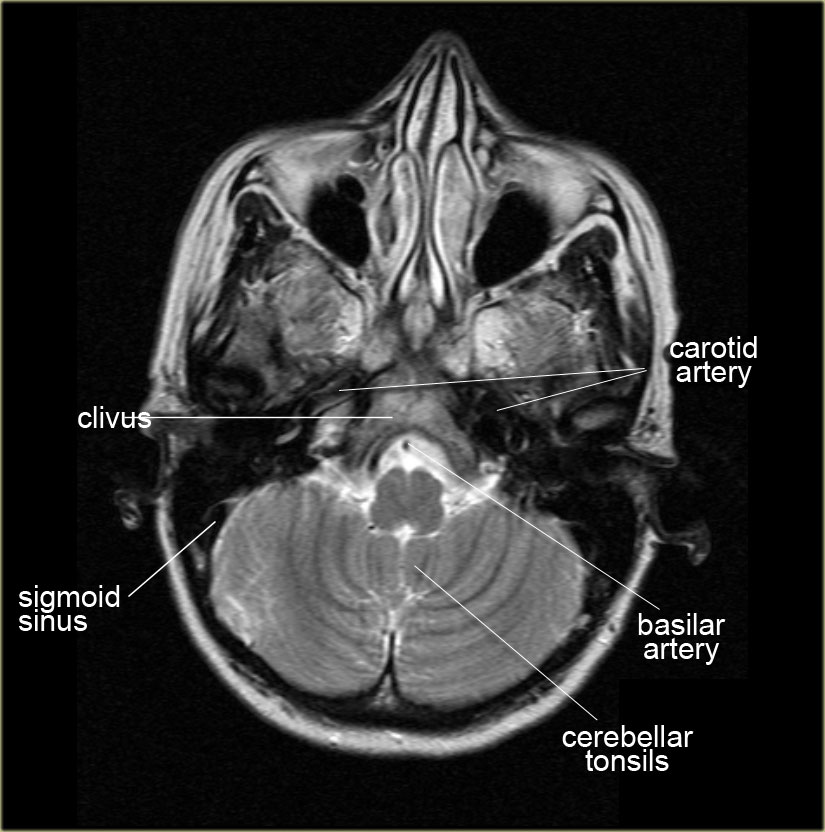
Scroll through the images on the left.
Specific regions
Circle of Willis
- A1-segment
Anterior cerebral artery from carotid bifurcation to anterior communicating artery gives rise to the medial lenticulostriate arteries. - A2-segment
Part of anterior cerebral artery distal to the anterior communicating artery. - P1-segment
Part of the posterior cerebral artery proximal to the posterior communicating artery.
The posterior communicating artery is between the carotid bifurcation and the posterior cerebral artery) - P2-segment
Part of the posterior cerebral artery distal to the posterior communicating artery - M1-segment
Horizontal part of the middle cerebral artery which gives rise to the lateral lenticulostriate arteries which supply most of the basal ganglia.
The M2-segment is the part in the sylvian fissure and the M3-segment is the cortical segment. - Cisterna ambiens
Also called ambient cistern is a cistern of the subarachnoid space between the posterior end of the corpus callosum and the superior surface of the cerebellum.
It is sometimes defined as including the quadrigerminal cistern.
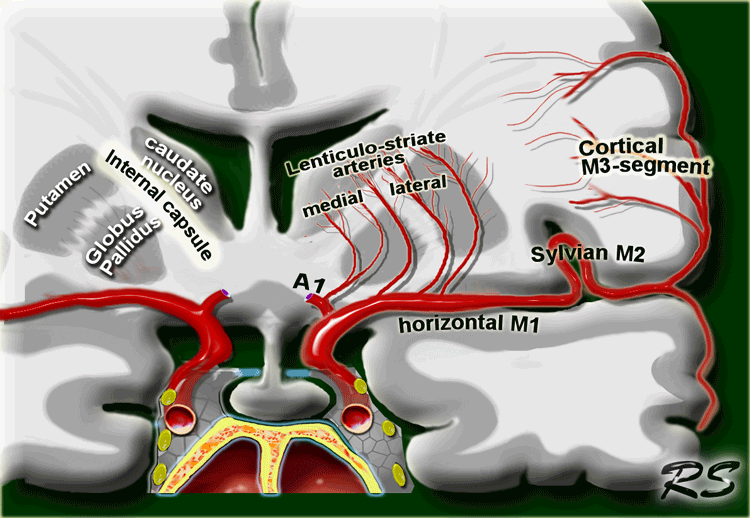
On the left a coronal view of the segments of the middle cerebral artery.
- Horizontal M1-segment
gives rise to the lateral lenticulostriate arteries which supply part of head and body of caudate, globus pallidus, putamen and the posterior limb of the internal capsule.
Notice that the medial lenticulostriate arteries arise from the A1-segment of the anterior cerebral artery. - Sylvian M2-segment
Branches supply the temporal lobe and insular cortex (sensory language area of Wernicke), parietal lobe (sensory cortical areas) and inferolateral frontal lobe - Cortical M3-segment
Branches supply the lateral cerebral cortex
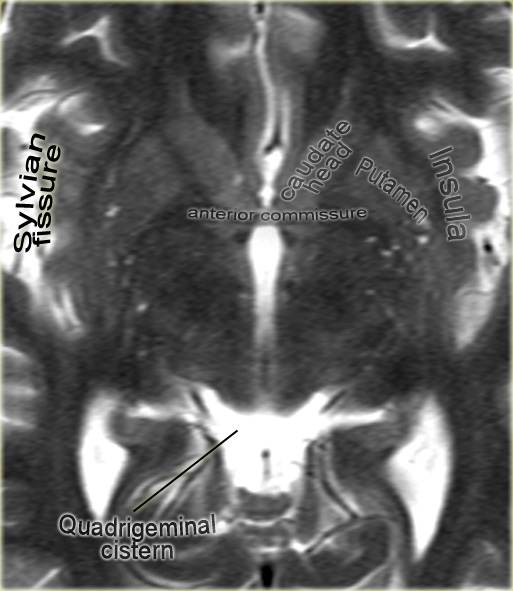
Anterior commissure
The anterior commissure is a bundle of white fibers that connects the two cerebral hemispheres across the middle line.
At this level frequently perivascular CSF-spaces of Virchow-Robin are seen.
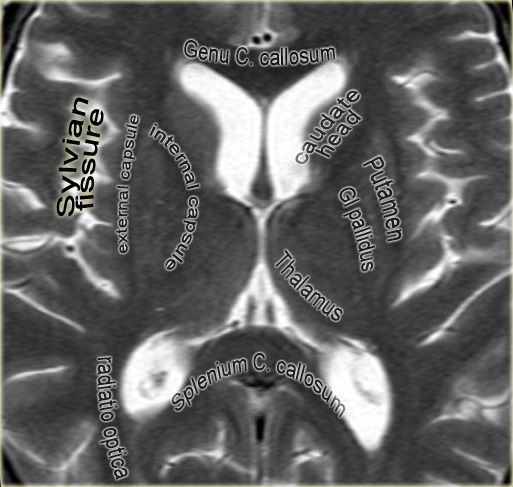
Thalamic level
At this level the basal ganglia are seen.
The two dark lines medially of the thalamus are the internal cerebral veins.
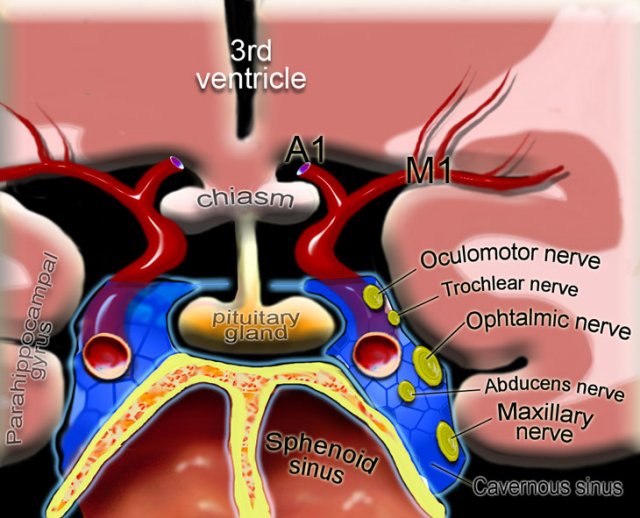
Pituitary gland
On the left a coronal illustration of the anatomy of the pituitary gland and the surrounding structures.
Read more about the pituitary gland in the article on sellar and parasellar tumors
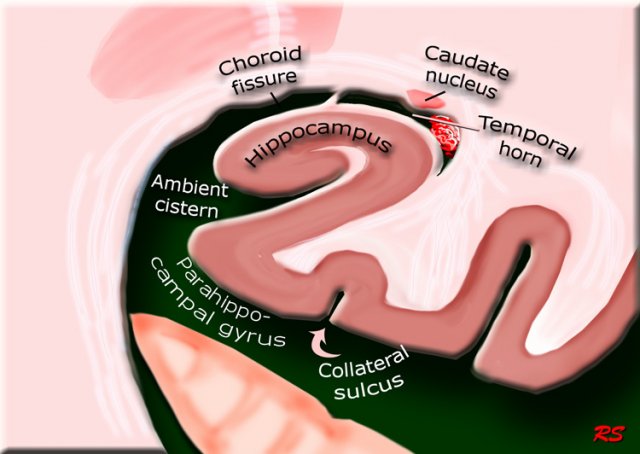
Hippocampus
On the left a coronal illustration of the area of the hippocampus.
Read more about the hippocampus in the article on the role of MRI in dementia