COVID-19 CO-RADS classification
COVID working group of the Dutch Radiological Society
Publicationdate
The CO-RADS classification is a standardized reporting system for patients with suspected COVID-19 infection developed for a moderate to high prevalence setting.
This is a proposed classification system for radiologists in the Netherlands and still work in progress.
Press ctrl+ for larger images and text on a PC or ⌘+ on a Mac.
This can be helpful for scroll-images.
Single images can be enlarged by clicking on them.
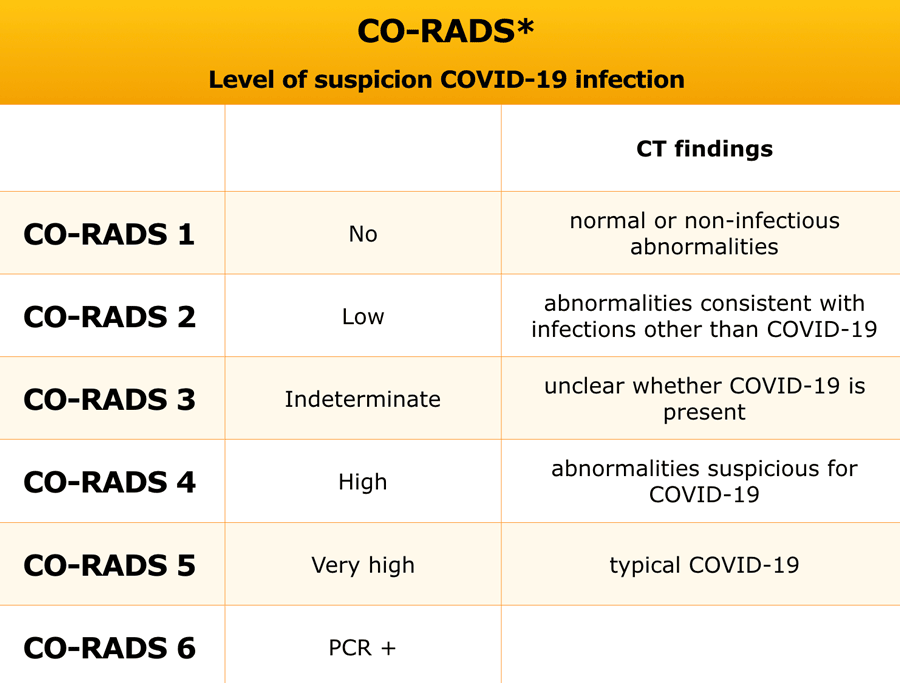
CORADS classification
Based on the CT findings, the level of suspicion of COVID-19 infection is graded from very low or CO-RADS 1 up to very high or CO-RADS 5 and the severity and stage of the disease is determined with remarks on comorbidity and a differential diagnosis.
Regular updates will be provided.CORADS-1 has a high negative predictive value in patients with complaints for four or more days.
CORADS 5 has a very high positive predictive value given the high a priori-chance in this epidemic.
The interobserver variation of CORADS 2-4 is still high and has a poor negative and predictive value.
The interpretation of the CT findings has to be combined with the clinical symptoms and the duration of the symptoms as a CT can be negative in the first few days of a mild infection.
Dutch version of CO-RADS:
https://www.radiologen.nl/system/files/bestanden/documenten/2020-03-29a_standaardverslag_covid-19_co-rads_ppt_pdf.pdf
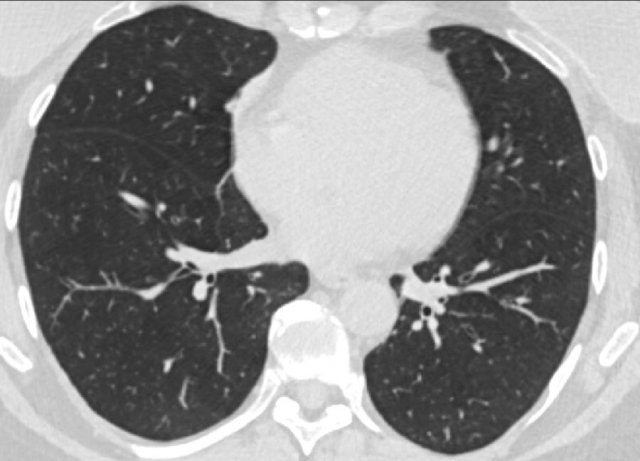
CORADS 1
COVID-19 is highly unlikely.
The CT is normal or there are findings that indicate a non-infectious disease like congestive heart failure, sarcoid, histoplasmosis, malignancy, UIP or fibrotic NSIP (if unchanged to prior examination).
An exeption has to be made for the first few days of a mild infection when the CT can be normal.
The CT-image is of a patient with complaints for five days.
There are no abnormalities and the PCR was negative.
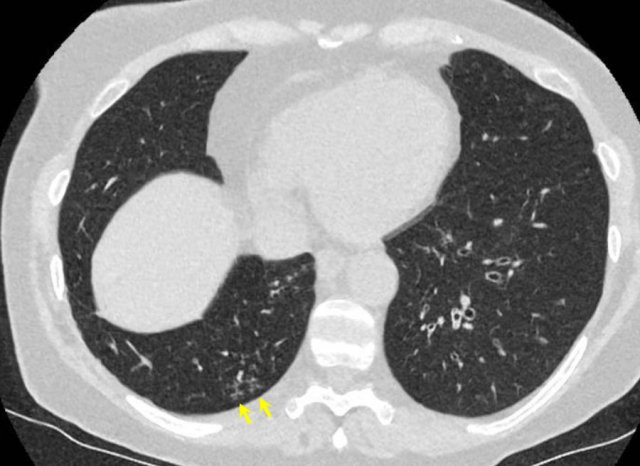
CORADS 2
Level of suspicion of COVID-19 infection is low.
Findings consistent with other infections like typical bronchiolitis with tree-in-bud and thickened bronchus walls, tbc.
No typical signs of COVID-19.
The CT-image shows bronchiectasis, bronchial wall thickening and tree-in-bud (arrows).
There are no ground glass opacities.
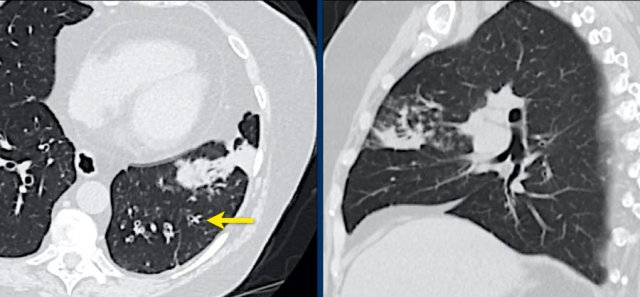
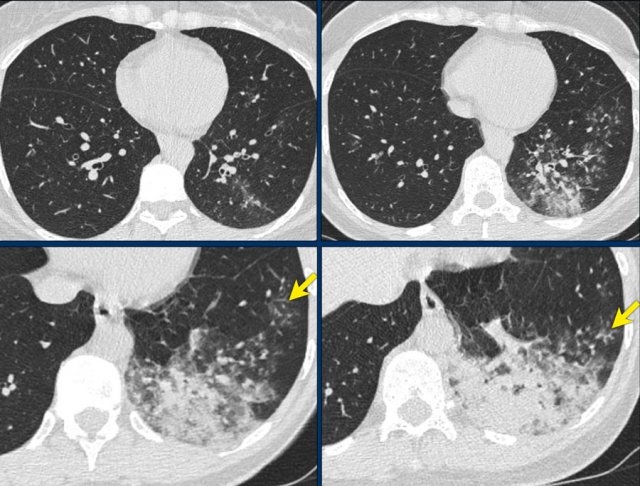
The images show bronchial wall thickening, tree-in-bud (arrow) and consolidation.
There are no ground glass opacities.
40 year old woman with fever and coughing.
CT findings: lobar consolidation and tree-in-bud (arrows) consistant with a bacterial infection, i.e. CORADS 2.
COVID-19 unlikely.
CORADS 3
COVID-19 unsure or indeterminate.
CT abnormalities indicating infection, but unsure whether COVID-19 is involved, like widespread bronchopneumonia, lobar pneumonia, septic emboli with ground glass opacities.
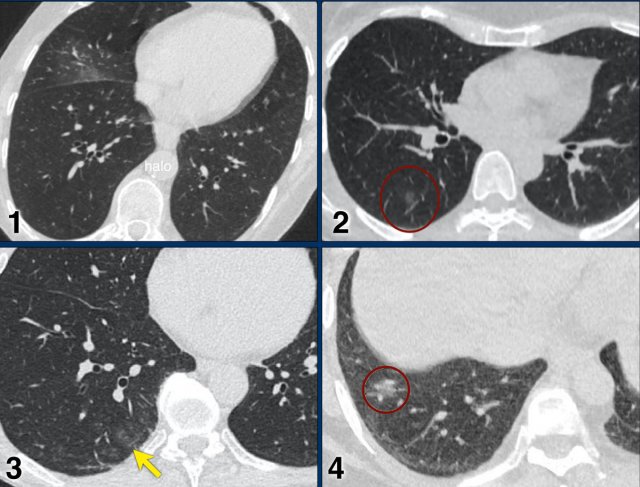
Case 1.
One day complaints. CT: Unifocal GGO. PCR negative.
Case 2.
CT: Unifocal GGO (circle).
Case 3.
CT: Unifocal GGO (arrow).
Case 4.
CT: Unifocal GGO (circle).
Case 5
7 day of complaints.
CT: multifocal consolidations with surrounding GGO.
PCR negative.
Case 6
Recent Influenza A . History of pulmonary hypertension.
Started coughing again.
CT: bilateral central consolidations with diffuse GGO.
Re-test: COVID-19 PCR: negative and Influenza A: positive.
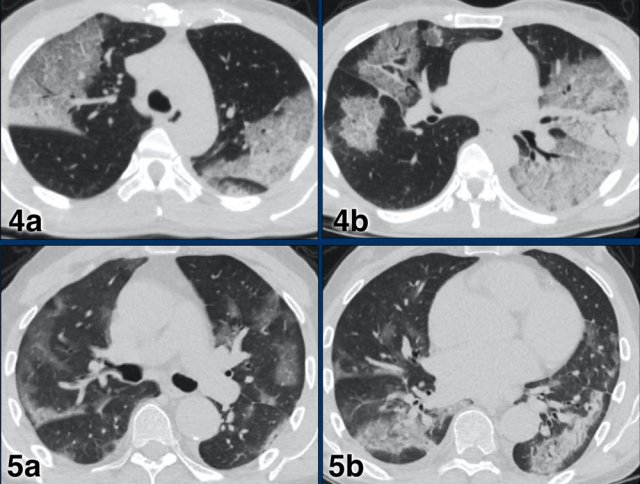
CORADS 4
In CO-RADS 4 the level of suspicion is high.
Mostly these are suspicious CT findings but not extremely typical:
- Unilateral ground glass
- Multifocal consolidations without any other typical finding
- Findings suspicious of COVID-19 in underlying pulmonary disease.
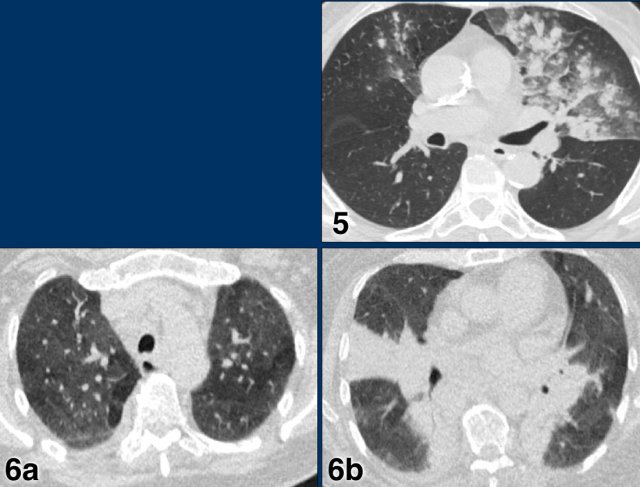
Case 1
7 days of compaints
CT: unilateral areas of GGO in left upper lobe.
PCR: positive.
Case 2
CT: bilateral GGO in a patient with emphysema.
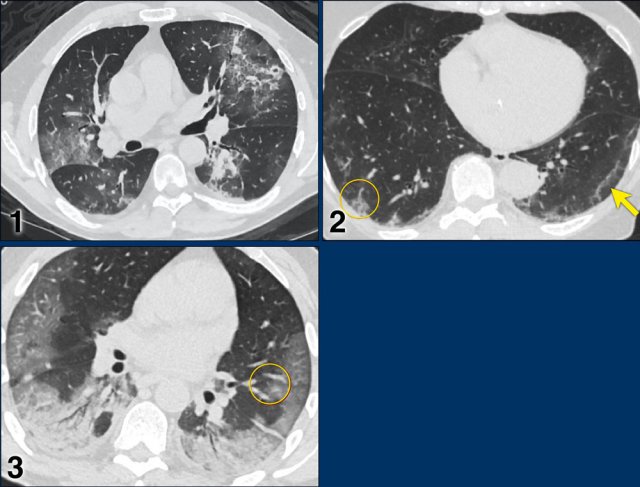
CORADS 5
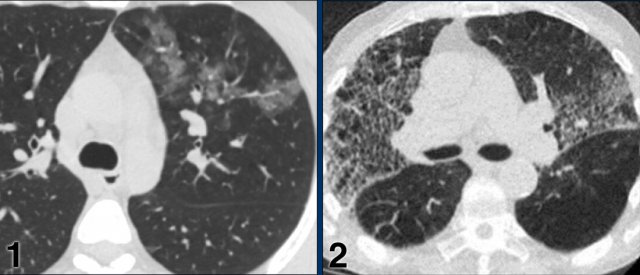
Case 1
Multifocal GGO and consolidation
Case 2
10 days of complaints.
CT: bilateral multifocal GGO, vascular thickening (circle), subpleural bands (arrow).
PCR: positive
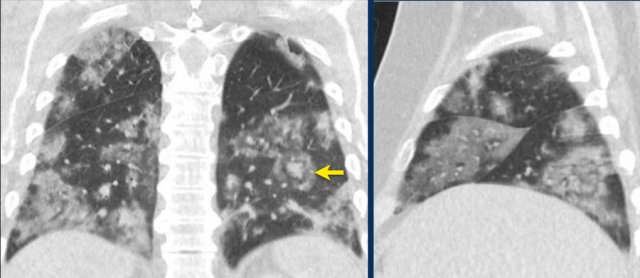
Case 3
Eleven days of complaints
CT findings: Bilateral GGO and consilidation, basal preference, vascular thickening (circle).
PCR: positive
Case 4
CT findings: multifocal areas of groundglass and consolidation
Case 5
CT findings: multifocal areas of groundglass and consolidation
CORADS 6
Patient with positive PCR and bilateral GGO.
Notice halo sign (arrow).
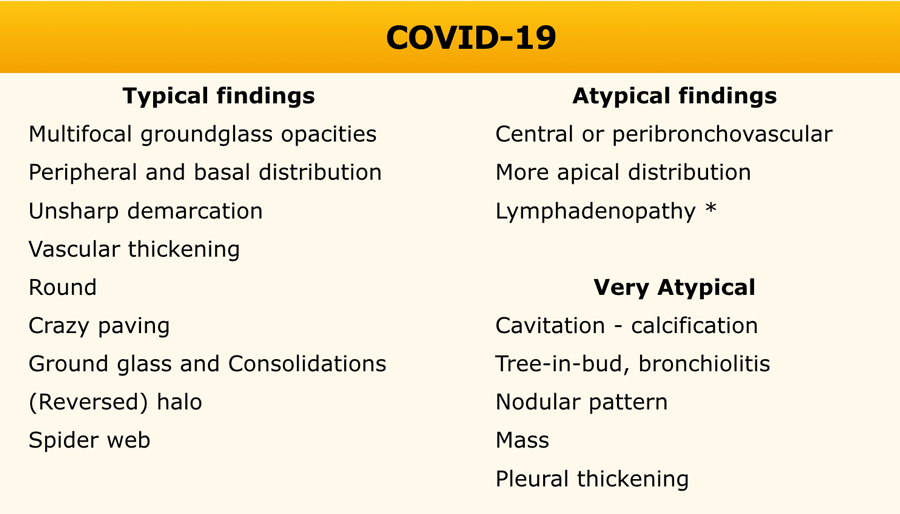
Typical findings
In the table the typical findings of COVID-19.
Mention findings that are very atypical, that are arguments against the diagnosis of COVID-19.
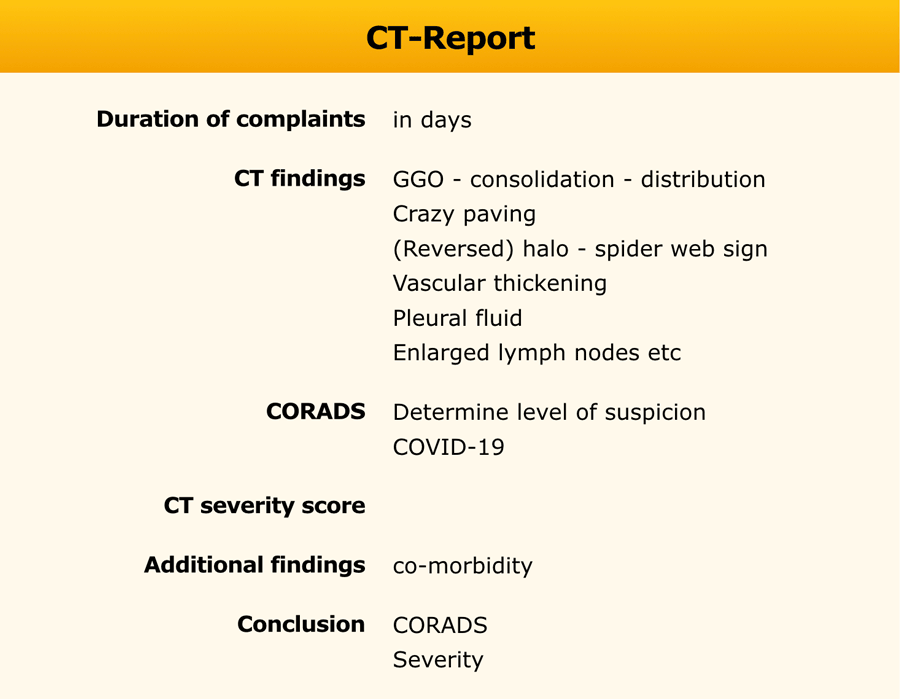
Report
The duration of the complaints is important as it determines the expected stage of the disease.
Discuss the findings, the chance of COVID-19 (CORADS) and the differential diagnosis.
The CT-findings of COVID-19 show overlap with other diseases like:
- H1N1 influenza
- Other viral pneumonia ; adenovirus, CMV
- Organizing pneumonia
- Acute interstitial pneumonitis